
In our work, titled ZenseTag, we develop a novel RFID-assisted sensing platform that connects COTS sensors to inexpensive, flexible RFID stickers. ZenseTag's key insight is a direct-to-RF interface for sensors, revealing that many commercial sensors have fundamental operational frequencies similar to antennas. This allows for optimal coupling with the RFID tag. We demonstrate robust sensor readout by having two RFID tags share the same antenna, enabling the reader to detect changes through channel differences. ZenseTag also incorporates high-performance software for low-latency, reliable readouts in dynamic environments.
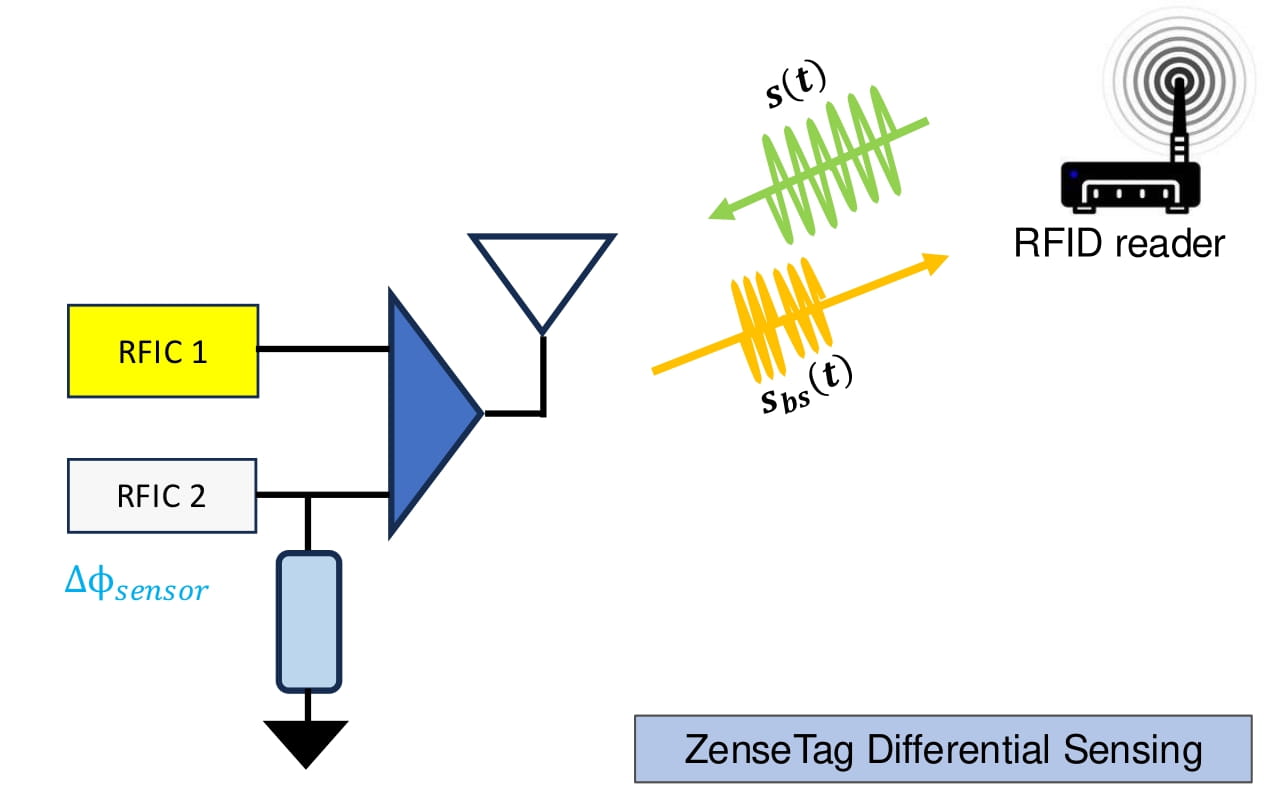
In this section, we outline the design steps of ZenseTag and its ability to interface various COTS sensors (force, soil moisture, and photodiode) with readily available RFID stickers. The key to this interface is ‘Direct-to-RF’ impedance profiling, modeling sensor behavior at 900 MHz. ZenseTag reveals that many commercial sensors have a resonant frequency that can be tuned to match RFID tags. We introduce a ‘Twin-Tag Single-Antenna Sensor Interface’ using flexible PCBs, allowing one tag to couple with the sensor stimuli while the other remains isolated. The RFID reader then detects channel differences between the two tags for low-latency, robust sensor readout in dynamic environments. ZenseTag's design encompasses three contributions: (1) Direct-to-RF impedance profiling to determine sensor resonant frequency, (2) Twin-Tag Single-Antenna Sensor Interface for tuning and interfacing, and (3) low-latency, robust sensor readout via custom software on a standard RFID reader.
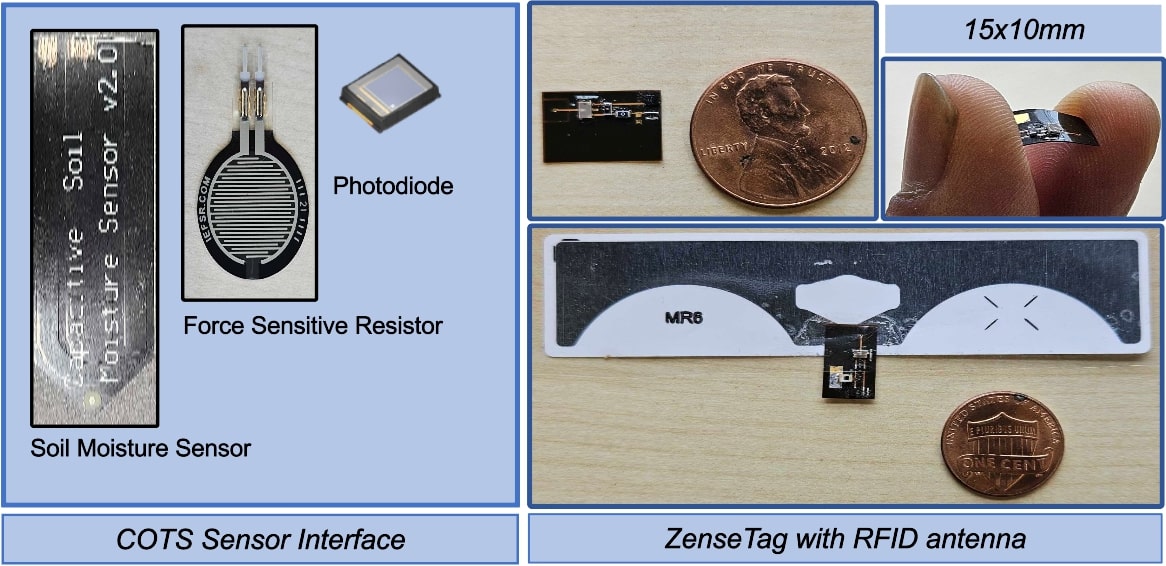
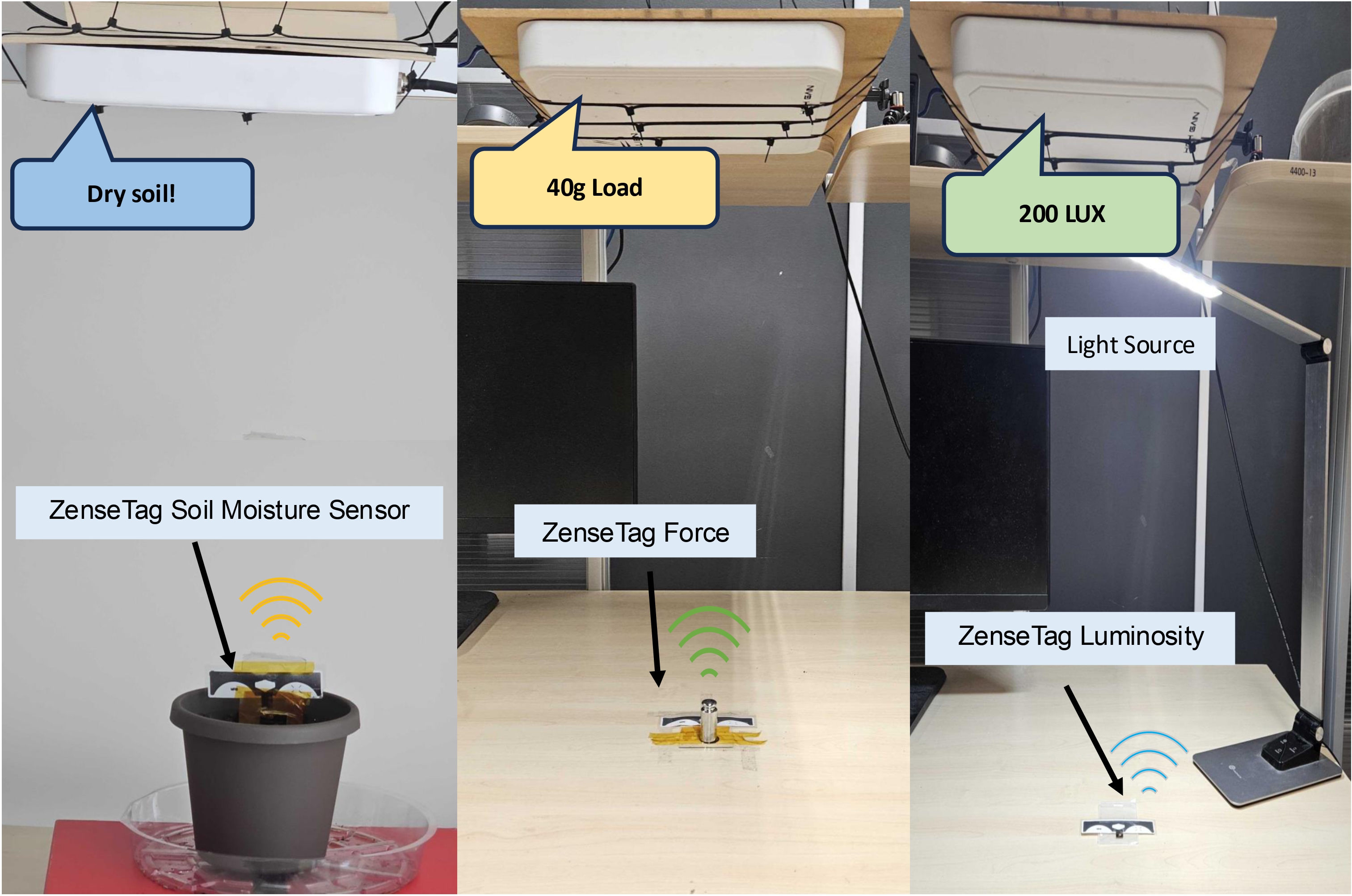
ZenseTag was evaluated using three commercial sensors: soil moisture sensor, force-sensitive resistor (FSR), and photodiode. For soil moisture sensing, after impedance profiling and resonance tuning, the system achieved a 15x improvement in phase change sensitivity and over 93% accuracy in classifying three moisture levels (Dry/Moist/Saturated). The FSR evaluation demonstrated detection of weights as light as 10g with a 30-degree phase change for 50g loads, while maintaining robust performance under dynamic conditions with less than 5-degree median phase error during human movement tests. The photodiode implementation successfully measured light intensity up to 400 lux with 96% accuracy between dark and bright conditions, and 90% accuracy between medium and bright levels, while also demonstrating wavelength classification capabilities between red, yellow, and blue light. All evaluations were conducted using a flexible PCB measuring just 15mm x 10mm interfaced with a printed RFID antenna and RFID ICs, maintaining the advantages of being battery-free and using minimal commercial off-the-shelf components.
|
|